...
previously if 10 users shared the same variable or restriction, it they would have to be added to each individual userwe needed to add that variable to these 10 usersuser
now we can create a role with this a variable , and restriction and if this the role is assigned to these 10 users, they all have this variable
the same concept applies to role restrictions
the variable and restriction would apply to all 10 users
Variables:
Global Variables - (existing) such a variable is available to every user
Role Variables - (new) if a role has variables, these variables are available to users if the role is assigned to a user
User Variables - (existing) a variable that is only available to a particular user
Variable Overriding:
Variables are applied in the following order:
User variables can override
...
Role variables
...
Role variables can override
...
Global variables
...
To help with understanding, if the let’s look at the following scenario. The system has been set up with:
a global variable PI_STYLES=default-theme (PI_STYLES represents the theme to be used to display the dashboard)
a role called Marketing, which has a variable PI_STYLES=marketing-theme
a role called Sales, which has a variable PI_STYLES=sales-theme
a user called Bob
Scenarios:
By who, by default, Bob has the PI_STYLES=default -themetheme
These variables will be applied in the following way:
If Sales role is assigned to Bob, Bob has will see the PI_STYLES=sales-theme
If the Sales and Marketing roles are both assigned to Bob , then the ordering position (newly introduced) of a role decides if , seen at the top-right of the Dashboard Configuration>Roles screen, will determine whether the sales-theme or marketing-theme them is used by for Bob
If the Sales role has a lower ordering position than the Marketing role (meaning it’s in the front of the queue), then sales-theme is used
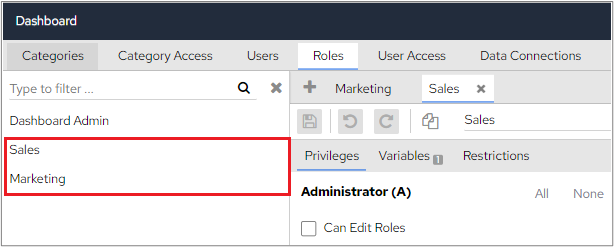
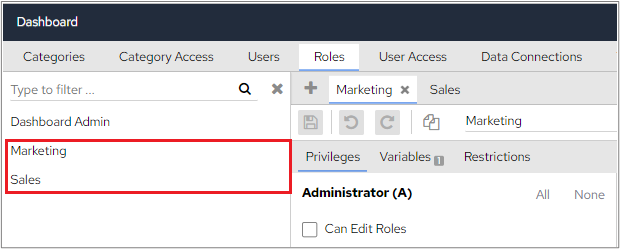
The ordering position also decides the display order of the Roles on the screen. Lower The lower ordering position is in the front. In the following example, the Sales role has the position 1 and Marketing is position 2 which means that the Sales role will appear above the Marketing role
If 2 roles have the same ordering position, then alphabetical order is respected both for display purposes and when role variables have conflicts. In the following screenshot, both roles have the position 1 which means they will appear alphabetically
If Bob has a variable PI_STYLES=bobs-theme, then bobs-theme would be used by Bob regardless if there is a role assigned to Bob
...
Role Restrictions - (new) If a role has a restriction, by giving such a role to multiple users can apply the same restriction to these users
User Restrictions - (existing) a restriction applies to a particular user
Restriction Cumulation and Overriding:
User Restrictions and Role Restrictions are applied to users, while:
when multiple roles are given to a user, with the same restriction, the restriction accumulates
when a user has a restriction, which is the same as a role restriction, the role restriction is ignored
To help understanding, if the system has:
a role called Marketing, which has a restriction: Department = 'Marketing'
a role called Sales, which has restrictions: Department = 'Sales'; Year = 2021
a user called Andy, which has a restriction: Region = 'UK'
ScenariosThen:
By default, Andy can only see data with Region = 'UK', because such a restriction is always applied to Andy
If the Sales role is assigned to Andy, then Andy can only see data with
Region = 'UK' (from Andy)
and Department = 'Sales' (Andy cannot see data related to Marketing)
and Year = 2021 (from Sales role)
If both the Sales and Marketing roles are assigned to Andy, then Andy can see data with
Region = 'UK'
and Department in ('Sales', 'Marketing') - (this is because Andy has 2 roles, so Andy can see data related to both roles)
and Year = 2021
If the user Andy has a restriction: Department = (‘Sales', 'Dev’), while Sales and Marketing roles are assigned to Andy, then the user restriction is used, and role level restriction of the same topic are ignored (the reason Department restriction from the role is roles are ignored, is because such implementation allows removing undesirable role restrictions)
Region = 'UK' (from Andy)
and Department in ('Sales', ‘Dev') - (from Andy, and ignore what’s in the roles)
and Year = 2021 (from Sales role)